AMMONIUM NITRATE SOLUTION
Overview
Ammonium Nitrate (AN) Solution is widely used as feedstock for the production of fertilizers or civilian explosives, being able to be used directly in liquid form, or processing it further to obtain a solid product.
When selecting an ammonium nitrate solution plant there are a number of choices to be made:
The first one would be the type of reactor, whether pipe reactor or recirculation reactor.
The neutralization reaction pressure selection is of paramount impor- tance firstly to ensure a safe operation, as well as to maximize the reuse of the process steam produced in the neutralization stage, in order to improve the energy balance of the plant.


The well proven technology, as well as the Flexibility to adapt to client requirements, are the key advantages of the ESPINDESA process.
Process Description
The required quality of Ammonium Nitrate Solution can be obtained by means of ESPINDESA process.
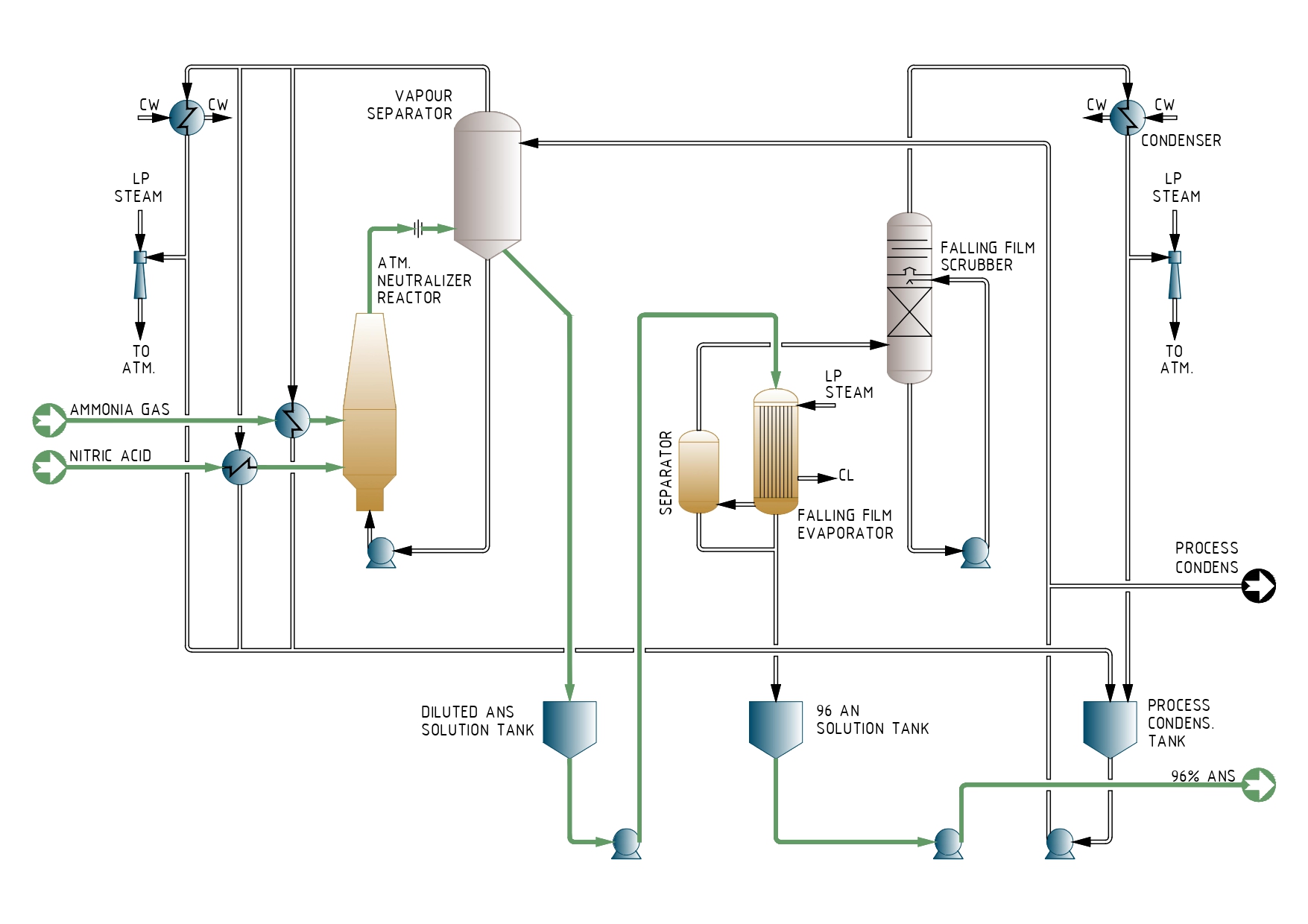
AMMONIUM NITRATE SOLUTION PROCESS DESCRIPTION
Neutralization Zone
Ammonia gas is mixed with nitric acid in a reactor, where the following reaction takes place:
NH3 + HNO3 → NH4NO3 + Heat
This neutralization reaction is done under a precise control of the ratio of each reactant, in order to achieve the optimum performance in the reactor, by performing a perfect mixing of the reactants and ensuring a safe operation.
This neutralization is an exothermic reaction that produces a great amount of heat, which is used to increase the temperature of the AN solution, while generating process steam, that can be used within the process.
The ammonium nitrate solution and the generated process steam are disengaged in the reactor. The resulting ammonium nitrate solution, with a concentration ranging from 78 – 92% depending on the operating pressure selected, is collected in a holding tank, from where it can be sent either to storage or to further concentration.
AN Solution Concentration Zone
In order to concentrate the Diluted AN Solution up to 96%, the Ammo- nium Nitrate is sent to a falling film evaporator, which operates under vacuum conditions.
The diluted ammonium nitrate solution feeding the Falling Film Evapo- rator falls wetting the walls of the exchanger tubes. The steam produ- ced during the AN solution concentration goes to a separator prior to be sent to a Scrubber, and the concentrated AN solution leaves the bottom of the Falling Film Evaporator and is collected in holding tank, from where it will be pumped to the final consumer.
Process Steam/Condensate zone
The AN content of the process steam (reactor process steam and falling film process steam) is lowered by a liquid washing of the process steam done in two stages in a Scrubber: first by washing this steam in a packing bed with diluted ammonium nitrate solution and later it is washed in several special trays using condensate as washing fluid.
The process steam leaving the scrubbers is then, if possible, used within the plant and the rest of process steam is condensed and collec- ted in a Vessel. This process condensate is further used by different consumers within the plant and the remaining condensate will be sent out of the plant for further use.
To improve the ammonium nitrate recovery within the plant, the purge of the scrubbers is recycled back the process.
Typical Operating Consumptions, per ton of product (as 100% AN basis)
Raw Materials
Ammonia 213 kg
Nitric Acid 789 kg
Utilities
Cooling Water 22.1 m3
LP Steam 33.5 kg
Electric Power 3.3 kWh
Process Flow Diagram
Process Description
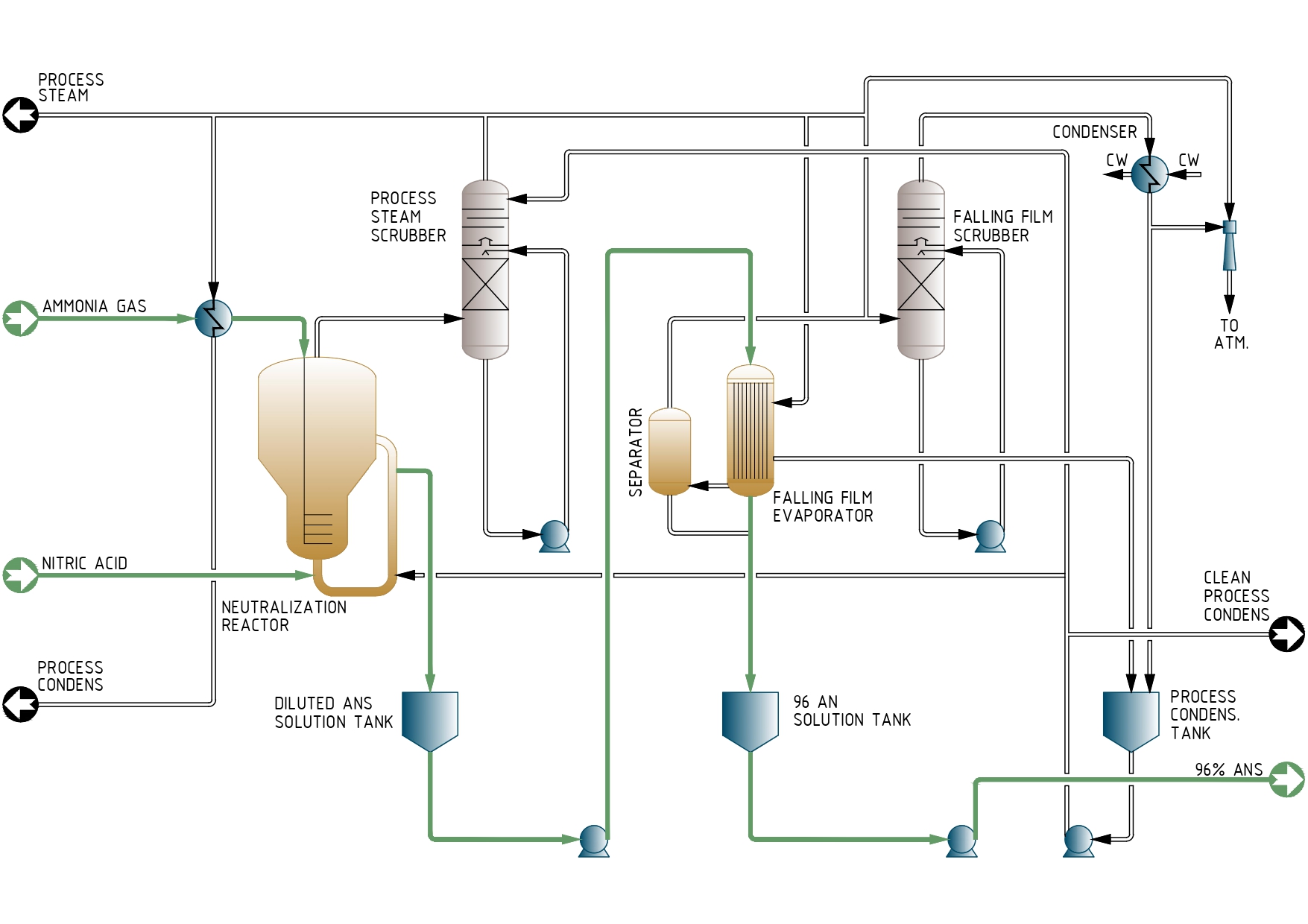
AMMONIUM SULPHATE NITRATE SOLUTION PROCESS DESCRIPTION
Ammonium sulphate nitrate (ASN) solution process can be divided into the following main areas described as follows:
- ASN 96 % solution production and concentration
- Steam treatment & distribution
ASN production by direct reaction of nitric acid, sulfuric acid and ammonia in the same reactor produces a huge amount of heat that is extremely difficult to control. In addition, the saturated mixture is exceptionally large corrosion potential. For this reason, direct neutralization within the reaction vessel is extremely restrictive, and it is preferred the alternative route where ammonia and sulphuric acid react in a reactor in presence of ammonium nitrate to produce ASN.
ASN solution production and concentration
AN solution is first diluted with process condensate in the AN Solution Mixer. Sulphuric Acid is also diluted with process condensate, being retired the heat of dilution in the Sulphuric Acid Cooler by means of cooling water.
AN solution and sulphuric acid are sent to the ASN Reactor, where both ammonia gas and sulfuric acid are also fed to react in the ammonium nitrate media, under agitation inside the saturator-reactor, according to the following reactions:
[1] 2 NH3 + H2SO4 → (NH4)2SO4 (aq) + Heat
[2] (NH4)2SO4 + NH4NO3 → (NH4)2SO4 • NH4NO3
[3] 2 (NH4)2SO4 + NH4NO3 → 2 (NH4)2SO4 • NH4NO3
Reaction [1] is highly exothermic; the heat of reaction released can evaporate the water contained in the sulfuric acid. The grade of the ASN produced depends on the extension of the reactions [2] and [3] (with molar relation AS / AN of 1:1 and 2:1 respectively)
Ferrous sulfate solution is dosed to the reactor to catalyze the formation of the double salt (NH4)2SO4 ·NH4NO3 and for pH adjustment.
For start-up purposes, the ASN solution from the reactor can be sent to the Evaporator Concentrator, working with low pressure steam as heating media, in order to remove the most part of the water. The evaporator – concentrator operates under vacuum; the vacuum in the area is produced by the Evaporator Steam Ejector; a flash is produced when the ANS solution is concentrated and steam is released and removed in the Evaporator Separator. ASN concentrated solution from the separator is sent to the ASN Buffer Tank, which is fitted with low pressure steam heating coils, from where it is pumped by means of the ASN Solution Pumps.
Steam treatment and distribution
The steam coming from the flash produced in the Evaporator Separator and the vapour from reactor are washed under vacuum conditions in the ASN Evaporator Steam Scrubber. In the bottom part of this scrubber, diluted ASN solution is recirculated by the Scrubber Pumps to remove most of the ASN traces entrained the steam. In the upper part of the scrubber, steam is washed in several trays with process condensate.
Afterwards it is condensed in the ASN Evaporator Steam Condenser with cooling water as cooling media and collected in the Process Condensate Vessel. This process condensate will be sent to the different consumers ISBL.
The purge of the scrubber is sent back to the reactor both to help keeping solids in suspension and to improve reaction yield, maximizing ASN production.
Typical Operating Consumptions, per ton of product (as 100% AsN basis)
Raw Materials
Ammonia (*) 160 kg
Ammonium Nitrate 385 kg
Sulphuric Acid 472 kg
Additive 9.6 kg
(*) The ammonia for Ammonium Nitrate Production is not considered.
Utilities
Cooling Water 11.7.m3
Process Flow Diagram