NPK STEAM GRANULATION
Overview
PROCESS FEATURES
- No need of phosphoric acid, which may not be available in some location
- The plants can manufacture a wide range of NPK formulations of high quality
- Low recycle ratio (1,5 to 2,5 depending on the formulation)
- Easy operationSmall use of sulphuric acid and ammonia
- It complies with strict pollution regulations
- Many different solid raw materials can be used, such as urea, ammonium sulphate, ammonium nitrate, TSP, SSP, MAP, MOP, SOP, etc.

Process Description
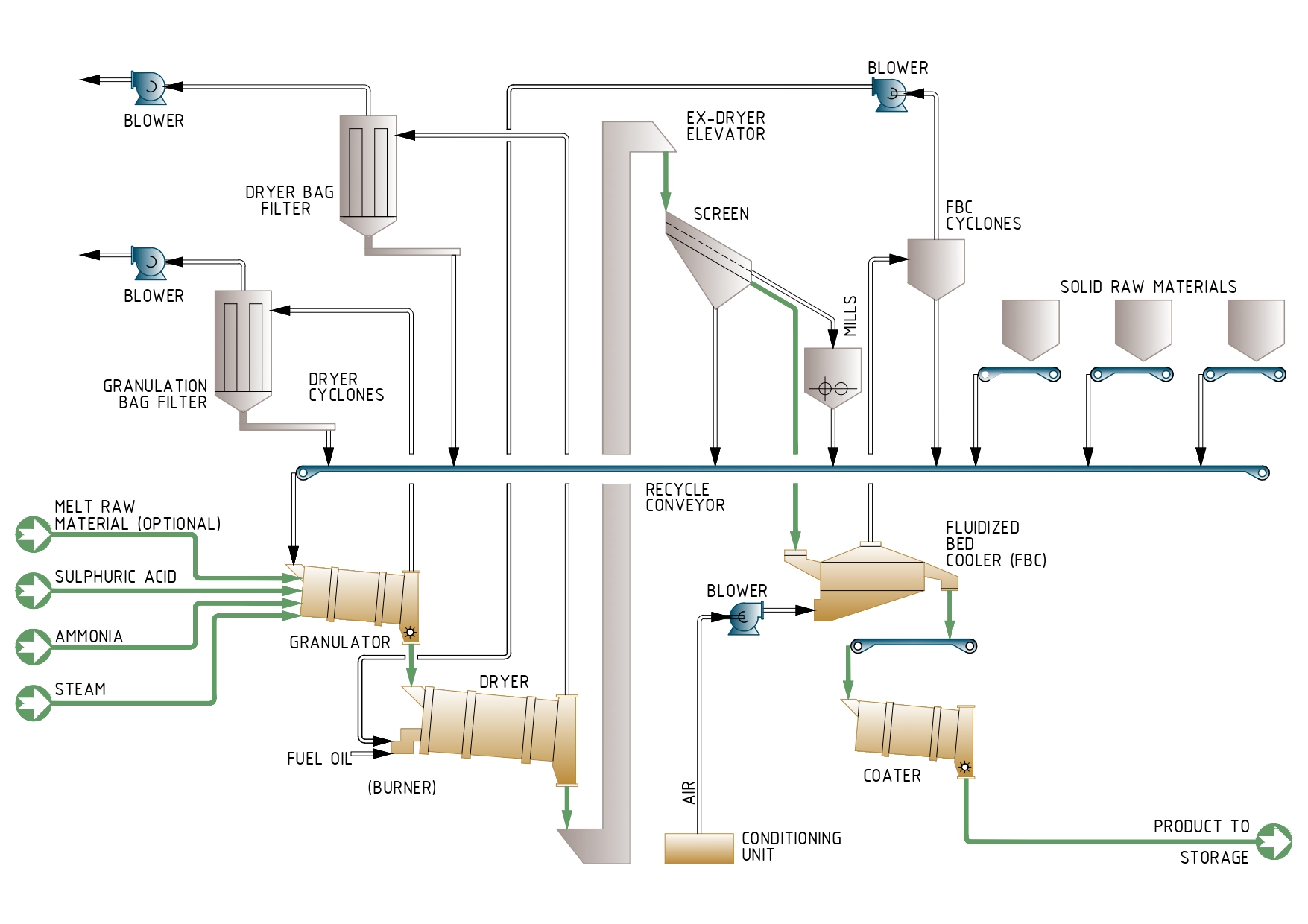
Solid Raw materials feeding
The solid raw materials (MAP, Urea, MOP, TSP, etc.) are fed to the appropriate raw materials hoppers and by means of variable speed Extractor Weight belts are fed into the granulator via conveyor where mix with the recycled fines.
Liquid raw materials feeding
Sulphuric acid and ammonia are fed to the granulator by means of spargers, together with some steam which supplies the necessary fluid phase for granulation.
The amount of sulphuric acid and ammonia is only the necessary to adjust the granulation temperature but in addition to this effect, the ammonium sulphate produced by the neutralization of the acid creates ammonium sulphate bridges which greatly harden the granules.
Solids handling
From the granulator the solids fall into the Drier where its moisture is reduced below 1%.
The dry solids are screened. The on-size solids are cooled and coated before being sent to the storage, while the oversize granules are crushed, mixed with the undersize particles and recycled to the granulator.
Bag filters are used to clean the granulator and Drier gaseous effluents.
OPERATING REQUIREMENTS
Raw Materials Consumptions
The efficiency of recovery of solid raw materials, measured as stack losses is as high as 99.5% while the recovery of ammonia and sulphuric acid reaches values of 99.0%.
Typical utilities consumptions (per metric ton of NPK)
Electricity 30 kWh
Fuel oil 5 kg
Process Flow Diagram