CAN GRANULATION
Overview
AMMONIUM NITRATE (AN) AND CALCIUM AMMONIUM NITRATE (CAN) AS DESCRIBED IN THIS BROCHURE, ARE, PRODUCED BY GRANULATION AND USED AS FERTILIZERS
The ESPINDESA process allows the manufacture in the same plant of different types of fertilizers based on ammo- nium nitrate, such as: ammonium nitrate 33.5%; calcium ammonium nitrate 26 – 20.5%. Even NPK fertilizers can be produced by the addition of other raw materials to the plant.
The Versatility is the key advantage of the ESPINDESA process.

High quality Ammonium Nitrate (AN) and Calcium Ammonium Nitrate (CAN) fertilizer grades can be obtained by means of ESPINDESA process.
Process Description
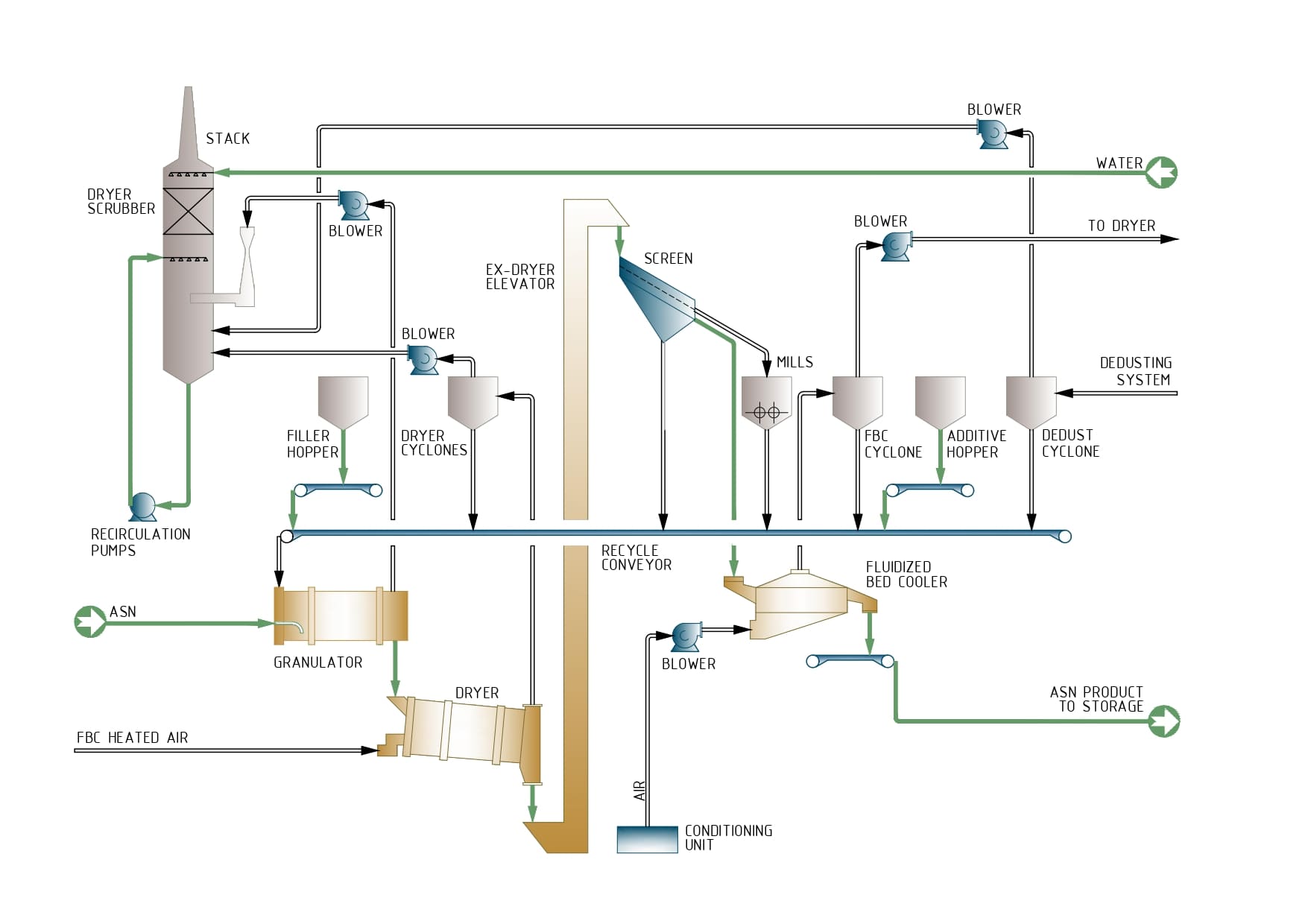
96% ammonium nitrate solution obtained in the AN Solution plant is pumped to granulation zone.
(for further information related to the AN Solution preparation, please refer to AN Solution Technology Sheet)
Granulation Zone
The production of Fertilizer Grade Ammonium Nitrate is carried out in a rotary granulator where the limestone or dolomite and the Ammonium Nitrate (AN) Solution are put in contact with the recycled material of the downstream sections.
Ferrous sulfate is added as granulation aids additive.
Heat required for granulation is mainly provided by the Ammonium Nitrate Melt itself, not only by the supplied temperature, also by the heat released during the crystalline transition of the AN.
By the combined effect of temperature, humidity and rotary motion, the mixture of the material produces granulation, resulting in the formation of round and hard granules.
The wet product leaving the granulator is sent to the Dryer. The distance between the Granulator and the Dryer should be minimized to avoid accumulation of wet product.
Granulation process is controlled by adjusting the following variables: concentration and temperature of AN solution, and solid recycle rate and temperature.
Drying, Screening, Conditioning and Coating zone
Drying of the granulated product is carried out in one step. The granulated product falls from the Granulator directly to the rotary Dryer, where the product comes in contact with a flow of hot air in co-current from the Dryer Heater.
Most of the water in the product evaporates to the desired moisture content.
In screening section, the solid is segregated into two fractions depending on the particle size: the oversized product is separated from the fine ones and the product in specification. Large sizes are fed to the Oversize Crushers, for size reduction prior to reprocessing, while the non-coarse fraction (fine products plus specification products) is sent to the second screening stage.
In the second stage mesh, most of the fines are separated from the product in specification to achieve the required output bulk size distribution of the product. The fines are collected on the Recycle Belt Conveyor.
To reach the required temperature of the final product to the warehouse, the product is cooled in the Fluidized Bed Cooler, which is fed with conditioned air.
The granules are fed to the two-stage Fluidized Bed Cooler (FBC), where they are cooled with conditioned air.
The exhaust air is sent to the Dryer. This process enhances the plant’s air and energy balance while minimizing emissions into the atmosphere.
The properly coated product is finally transferred to the final storage via the Final Product Conveyor.
The plant is designed with a high-efficiency dust extraction system to ensure a clean working environment during solids handling. It is a vacuum collection system with air inlets at the dust production points to prevent dust from escaping to the plant..
Product Specifications (typical)
| CAN | AN | |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen content (% by weight) | 20.5–26 | 33.5 |
| Moisture content (% by weight) | ≤ 0.5 | ≤ 0.25 |
Utilities Consumption
Steam 30 kg
Cooling Water (DT: 10ºC) 15 m³
Electricity 30 kWh
Process Flow Diagram
In addition to the CAN granulation process, for ASN Granulation process the same equipment configuration can be utilized to process ammonium sulphate nitrate solution, producing a solid fertilizer